Designing for superior business performance
A guide for technology, creative and startup leaders
Phase 1 - Unify understanding of strategy
When people are asked:
- What is a business strategy?
- What is the purpose or value of having a business strategy?
- What is the difference between a strategy and a plan?
many people have great difficulty in providing any clear answer to some and often all those questions. Many aspirational product teams and leaders understand they are supposed to have a strategy, but are unsure of exactly what it is, or how to create a one that can enable the success the team desires. Consequently, even with one of the most educated and hardworking workforces in history, so many businesses and business units are struggling to make an impact, even with high workloads and considerable dedication.
Strategy creates focus, through choices, focussing resources on the most substantial opportunities. Rather than trying catch a thousand minnows, catch a one to a few substantial opportunities.
Challenge for you
In a light-hearted way ask your team specifically, what is business strategy or what is the purpose of business strategy. If the answers are inclusive of fuzzy statements similar to:
- It sets the direction (strategic direction)
- Establishes the priorities
- It is about the long term
- It defines the vision and the mission
- Defines what we want to achieve in the long term
- It is how we bring our vision to life

You can introduce your team to this guide. Why?
Whilst the above statements may be represented of some concepts of a strategy - none of these are specific enough to create a complete high performance business strategy. Moreover, a well considered business strategy like that which you can design in this guide will deliver substantially more opportunities and clarity than these vague statements represent.
Is strategy still relevant?
As the creators of the StrategyCAD™ platform this is a question and assertion regularly encountered. This kind of question can only be asked by those who do not understand strategy as a business design activity, and usually by those who practice strategy as a planning activity. They ask based upon their experience of how their organizations practice strategy. But real business strategy is designing a value proposition and its delivery system to enable a business to offer superior value to its rivals. The question back to those who ask this question is, how could it ever be irrelevant?
Challenges or opportunities continue to abound including globalization, geopolitics, social media, the internet, digitization, computer automation, artificial intelligence and so on.
For some it can all seem rather hopeless to have any aspiration of a viable and sustainable strategy, but it is indeed these kinds of changes that make it more important than ever to have a well-defined and then managed business strategy. Either be part of the wave of new opportunities or be run over by them, so to speak.
Enduring strategies
Many companies have and continue to have strategies that sustain their value and relevance to the community they serve including Accenture, Adobe, Apple, Bank National Parias, Berkshire Hathaway, BMW, Citigroup , China Mobile, Coca-Cola, Daimler, Deloitte Touché, Ernest and Young, Goldman Sachs, Harley Davidson, Honda, IKEA, John Deere, Johnson and Johnson, KPMG, Kia, Microsoft, Nestle, Paccar, PEPSI, Proctor and Gamble, Samsung, Southwest airlines, Suzuki, Toyota, Volkswagen group , Wells Fargo, Walmart and of course tens of thousands of other businesses worldwide evolve their strategies and sustain relevance and value.

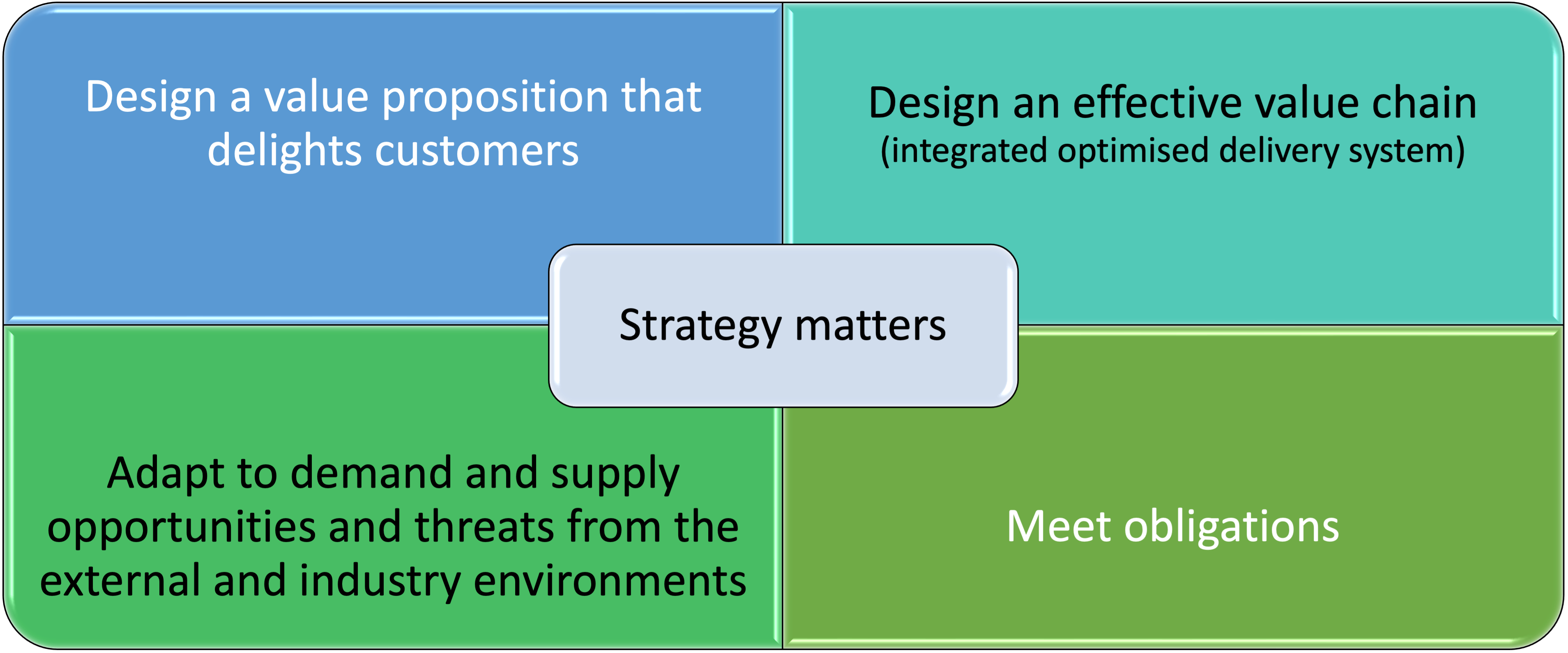
A business strategy defines why the business exists and then completes a very specific set of choices that represent how it is going to succeed. In the absence of that too many business and business units lack an architecture or a blueprint for what success looks like and how they will achieve it. A mission and vision statement with a to-do list is not a strategy and not a substitute for one. In the absence of a blueprint for the business, any idea can seem like a good idea. Consequently, people end up working on a huge variety of initiatives. However, the initiatives frequently lack synergy with the few things that really make a difference in sustaining business value. These things that matter are:
Designing and sustaining a value proposition that delights some segment of a market or markets
Satisfied customers may like your business, delighted customers love your business.
Designing and sustaining a unique and effective (time, cost, and quality) system to deliver that delight.
You can apply Porters value chain, which has stood the test of time for nearly 3 decades.
Ability to understand and adapt both the value proposition and the delivery systems to changes in the business environment.
Use a structured approach to identify opportunities and threats for your value proposition and business.
Managing risk along with meeting regulatory, legal, social, and other obligations.
A gentle but useful beginning
In this guide you will address all the items above. Firstly you can make sure you have clear answers to those first few questions.
What is a business strategy
What is the purpose or value of having a business strategy?
What is the difference between a strategy and a plan?
A unified understanding of these questions will ensure subsequent chapters make sense. In the first chapters you can review what strategy is and what it is not.
Building a high performance strategy
With these questions in hand, this guide will introduce
How to assess, understand and identify opportunities and threats from the environment your business operates in
How to design a value centric business.
The purpose of a business is to create a customer, and to have customers we must create value and ideally unmatched value for some segment of a market. The additional interesting opportunity in this chapter is using the same principle of value at the center to engage and empower people in the organization to succeed.
How to use a strategy kernel to bring your business design to life
How to create an integrated set of objectives consistent with the policies in the strategy kernel to focus time, talent, resources, and effort toward the opportunities that will make the biggest impact on business performance.
Feel free to work your way through this guide in order or your own order and then refresh any area you wish to revisit. Later sections will assume some knowledge of earlier sections.
Guide navigation
You can expand the accordions below to review the content benefits of each section. Each accordion allows you to navigate directly to that section.
In this section you will get
An understanding what business strategy is and what it is NOT.
HINT: It is not mission, visions and goals. That is goal setting, goal setting is part of strategy, but it is not a substitute for it.
Classic and more contemporary definitions of what business strategy is
Definitions create clarity
A deeper and guiding understanding about why strategy matters
Its more than direction, it's how you can succeed.
- The difference between a strategy and a plan?
You may never utter the words strategic planning ever again
Playlist
What exactly is business strategy?
You will be surprised how many people struggle to clearly and simply define what business strategy is and why it is essential to have one.
This section should remove any ambiguity that is confusing you or your team.
What does competitive advantage mean and why does it matter?
Competitive advantages can be transient or enduring either way it is a significant purpose of business strategy.
What is Competitive advantages and why does it matter to your business?
The most exciting secret to guide your business strategy?
Business is more like art than a competitive sport. Keep this in mind during your strategy development
Find two essentials of strategy that enable you to move forward easier in any competitive environment?
The types of strategy available and more reasons strategy matters?
Conceptually business and business strategy is simple. There are only 2 or at best 3 business strategy patterns to choose from.
Knowing the type of strategy pattern you are using is a super helpful
frame of reference to guide making your strategic choices.
Conclude this section with a few more bits about why
having a strategy in any pattern
is essential for your business.
In the section you can
Review some of the common barriers to a quality business strategy.
Consider or identify some of your own barriers to creating a complete business strategy.
Playlist
Lack of understanding of what strategy is and its' purpose?
Strategy as buzzword has confused its definition and purpose.
Use this knowledge to prevent you or your team from misunderstanding strategy.
Strategy requires two things that take courage.
Find out what they are, so you can create such courage in your team?
Productivity ultimately means achieving desired outcomes with fewer resources (time, money, consumables)
When outputs and activity are confused with productivity strategy can suffer. Use this knowledge to support creativity for breakthough productivity.
Creativity is valuable, but it is faster and easier if there is a base recipe.
Stupid ideas that have undermined strategy but made their way into popular scarcity business thinking.
Too many people think strategy requires a business degree. Hopefully, this little section helps dispell this myth.
In the section you can
Get introduced to the strategic choices (design decisions) every business leadership team must make and keep current.
Provide the authoritative source for these choices
Get introduced to how to link these design choices and then how to bring the design to life via the Strategy Kernel.
This section .
Playlist
Select the video to play
In the section you
Get introduced the strategic choice of Aspiration.
Define your customer aspiration(s)
Define your business aspiration(s).
In this section you can.
Make your aspirations more tangible by identifying the measures that you will use to measure your customer and business aspirations.
Define your KPI's usually trailing indicators of performance e.g. customer satisfaction, net profit, total sales etc
Define your business drivers usually activity based leading indicators of KPI performance e.g. number of customer follow-up calls, percentage of full sales versus discounted sales, number of sales leads gathered,
If you think of your business or value proposition (subsequent chapter) as a being a seed, then the arena is the field where the seed is to be planted. In the right field with the right seed, the business / value proposition can bloom, in the wrong field it may struggle to thrive.
In this chapter you can assess your existing arena or define a new arena. You could define a new arena for a new business or to launch a new product or expand an existing product. This chapter gives you the information and tools you will need to be able to establish and then maintain an understanding of how fertile an arena is. With this understanding you can decide whether to continue or start planting in an arena or plant elsewhere.
Different industry segments can be easier or difficult to succeed in. The go-to method for assessing an industry segment attractiveness or find a way to make it attractive for your business is Porters Five Forces assessment tool.
Will you use this tool every day? Almost certainly not. However, lacking knowledge of it is a tremendous disadvantage and having the knowledge of it, will give you a tremendous advantage in understanding what existing or changes in industry structure may mean for:
- Profitability
- Demand for products or services from your business or the industry as a whole
- Production costs
Playlist
Select the video to play
Why do you care about assessing the forces that affecting industry profitability
Assess the threat level of new entrants.
In what situations are new entrants more likely to threaten the profitability of an industry segment. How do you defend against new entrants or enhance your chances of success by being one?
Assess the profitability threat level of buyer bargaining power.
In what situations do buyers have the bargaining power. How can you defend against buyer bargaining power?
Assess the profitability threat level of supplier bargaining power.
In what situations do supplier have the bargaining power. How can you defend against supplier bargaining power?
Assess the profitability threat level of substitutes.
In what situations do substitutes offer the most threat?
How do you respond?
Assess the profitability threat of rivalry
In what situations does rivalry become
most of threat?
How do you respond?
Assess profitability opportunities from complements
What are complements?
Can you create complement opportunities?
Opportunity awareness enable your business and value proposition to skate to where the future needs and demand are likely to be.
Threats are conditions that threaten your value proposition's profitability, supply or production costs or even the viability of the entire business.
The more proactively these are identified and managed, the better the performance the business can enjoy.
In this section you will be able to effectively and continuously assess for opportunities for and threats to
- Profitability
- Increase demand for products or services will likely be
- Optimize production costs and supply
Playlist
Why search for opportunities and threats
Why do you care about assessing the forces of change in the external environment.
Why so many business leaders miss these
Why do so many leaders miss opportunities and threats.
Introduce PESTELG as a method to search for opportunities and threats.
Describe the PESTELG framework and its role in opportunity and threat identification?
Assess the political influences on future demand and supply.
Based upon political influences what future opportunities and threats might be available?
Assess the economic influences on future demand and supply.
Based upon political influences what future opportunities and threats might be available?
Assess the social influences on future demand and supply.
Based upon social influences what future opportunities and threats might be available?
Assess the technology influences on future demand and supply
Based upon social influences what future opportunities and threats might be available?
Assess the environmental influences on future demand and supply.
Based upon social influences what future opportunities and threats might be available?
Assess the legal influences on future demand and supply.
Based upon legal influences what future opportunities and threats might be available?
Assess the global influences on future demand and supply.
Based upon global influences what future opportunities and threats might be available?
Assess and prioritize opportunities and threats.
Based upon potential opportunities and threats evaluate and prioritise these?
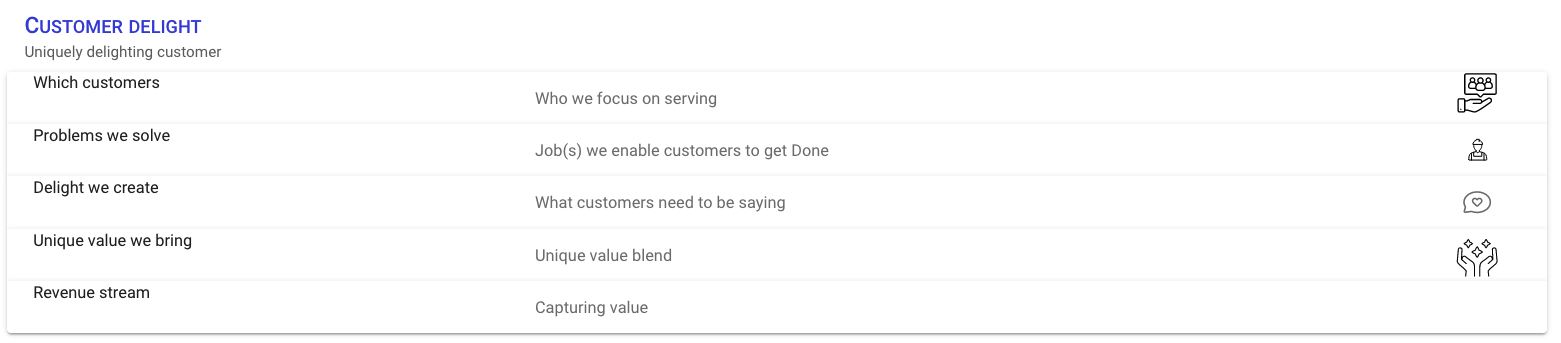
Satisfied customers like your business, value proposition and brand. Delighted customers love your business, value proposition and brand.
Using this choice we aim to go beyond the basic Unique value proposition design - adding considerations for creating delight.
It is a longer journey in this chapter than the others. But you will refresh or orient your understanding of everything from market definition, segmentation, targeting and positioning along the Jobs to be done and needs recognition and more.
Playlist
Choice 3: Delight we create - Introduction
Introduces the relevance and importance of delight versus satisfaction.
Provides an overview of the steps to work through to engineer delight and an additional attribute of your value proposition..
A value proposition must answer the question, what needs are being met by the value proposition. This is section defines what is meant by needs / motivations.
Identifying needs with the Jobs to be Done framework.
Introduces and provides an example of using the innovative Jobs to be Done framework created by the great Clayton Christensen to not understand needs but understand them completely and the situations that trigger them.
Market segmentation to identify customers with the needs your value proposition satisfies
Use the StrategyCAD target situation definition framework applied to business performance to collaboratively define where organizational enablement needs to be
Market segmentation to identify customers with the needs your value proposition satisfies
Identify which segments to target based on their attractiveness.
Inform targeted segment(s) to make your value proposition understood, differential, valuable or uniquely appealing
Review your Which customers of defining your value proposition - segmentation, targeting and positioning choices
You have defined which customers, the problems you solve and the range of needs you will meet. Now it is time, to apply End in Mind thinking. What do customers need to be saying about your value proposition to fulfill your customer and business aspirations?
From your understanding of your target market segments, real or imagined customer narratives. Define the unique combination of attributes of your value proposition that will create delight?
Review the options and identify the revenue model(s) to capture value from your value proposition?
In this section you use the knowledge built up in the
-
Where we play and
-
Delight we create
choices to guide strategic choices about what types of products and
services your value proposition is
going to provide.
.
Additionally, you can identify the channels your business will use to promote
awareness, sell, deliver, and support your offerings.
Finally, at your discretion you can add some narratives that explain these
choices and their synergy to your earlier choices.

Playlist
Select the video to play
Introduction and objectives for the choice related to solutions we provide strategic choice.
Define the strategically significant attributes of your offerings.
Define the purpose, objectives, vision and important willingness to pay and quality attributes of your offerings within your value proposition.
Define the consumption chain associated with your offering.
Discover and identify potential differentiation by defining your customer’s entire experience with your product or service.
Use StrategyCAD to define a structured channel strategy to connect your value proposition to the consumption chain defined in the previous step.
Simple, but necessary
The purpose of this section is to explain.
- How you create an account for StrategyCAD.
- How you manage team members to your account.
- How you provide feedback and get support.
Playlist
Select the video to play