Designing for superior business performance
A guide for technology, creative and startup leaders
Choice 2: Where we play - new entrants
Assessing threat of, protecting against new entrants or becoming one
In this chapter
Overview of what is the threat of new entrants
Factors that reduce the new entrant threat.
Protecting against new entrant threat
Overcoming new entrant barriers
Tools that can help build and sustain your understanding
Introduction
As an industry starts to become attractive, then more businesses will be keen to get some action. In declining industries there is less threat of new entrants. Threat of new entrants increases as barriers to entry are reduced. Barriers to entry are elevated by factors such as:
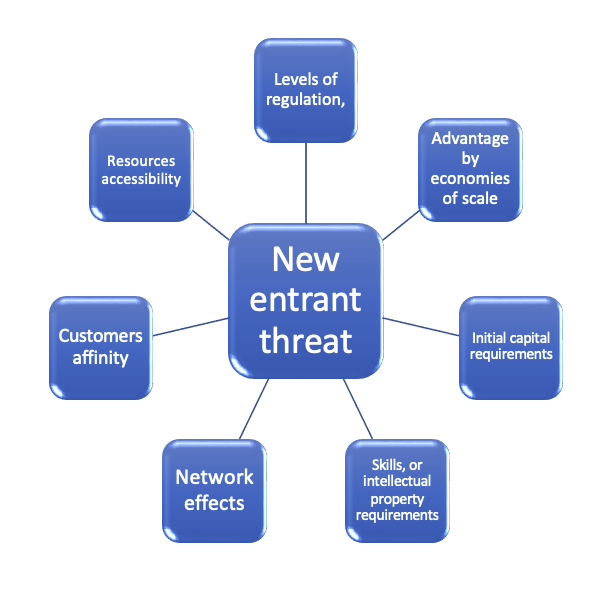
Reducing the new entrant threat levels.
High levels of regulation.
Difficulty competing without the economies of scale.
High initial capital requirements.
Advanced skills, or intellectual property to create the business.
Diminished growth in the industry
Sticky customers i.e., inconvenient, or costly for customers to change
Limited access to enabling resources e.g., a diamond mine or patent protected intellectual property
Positive Network effects - the more users of a product or service the more valuable it becomes.
Review of new entrant threat factors
Most of these elements are somewhat intuitive, so you can review these factors briefly here before we move on creating and overcome new entrant barriers.
Regulation
Industries with strict government regulation pose a higher barrier to potential new entrants. If regulation is increasing barriers to entry increase. If regulation is decreasing barriers to entry decrease too.
Economies of scale
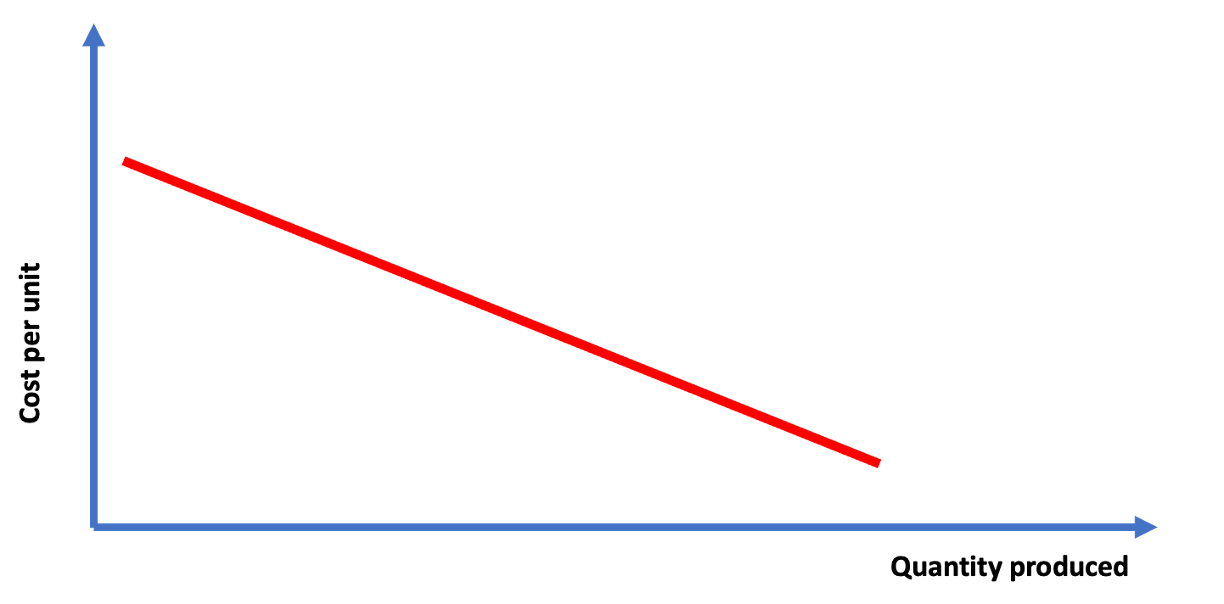
Economies of scale are often influenced by fixed costs. For example building a semi-conductor
plant is very expensive with high fixed costs. However, the input (variable)
costs
of creating the chips is low - hence to succeed in this type of industry
economies of scale are advantageous - that is variable costs do not increase
much as you increase volume and overall units costs are reduced as quantity increases.
(Because now the fixed costs are being divided by more output so unit prices are being
reduced).
Alternatively, stated, a business can increase volume
without increasing costs at the same rate.
Hence, to defend against new entrants, incumbents with an economy of scale
advantage can increase volume, increase supply in the market,
which reduces prices and squeeze new players out of the market.
New entrants are squeezed as their offerings
are now relatively expensive and they cannot compete on economies of scale.
High fixed costs
Does the new entrant require high fixed costs in things such as specialist equipment, properties, and land are examples of high fixed costs or is technology reducing the fixed cost requirements.
Is there a high cost of obtaining other resources to deliver required value? For example, a new entrant going up against eBay or Alibaba, they need to endure the cost of acquiring sellers to attact buyers. Without buyers the sellers will be reluctant and hence there could be high a cost to grow each side of the platform.
Constrained skills
When entering an industry requiring specialized and constrained skills or techniques, there is a higher barrier to entry for potential entrants. For this criterion consider are the skills required to be effective in the industry increasing, decreasing, or staying the same? Are these skills becoming more, less or the same availability? If the availability of skills is increasing, then the barriers to entry for new rivals may be reducing increasing the threat of new entrants.
Constrained access to resources
When entering an industry requiring specialized and constrained resources,
there is a higher barrier to entry for potential entrants.
For this criterion consider are the essential resources required
to be effective in the industry? Is the resource accessibility
increasing, decreasing, or staying the same?
If the availability of resources is increasing, then the barriers to entry for new
rivals may be reducing which in turn means increasing threat of new entrants.
Commonly, occurring examples are Patents and the expiry of patents.
Once a patent expires on a drug, for example, then new entrants will enter, as a
resource intellectual property protection no longer applies.
Historically, large corporations had controlled the
communications and distribution resources associated with global supply chains.
Given this control, it was difficult for small and mid-sized businesses to
participate globally.
However, with the combination of global communications and vastly more open
global distribution channels, those constraints declined and levelled the global
supply playing field.
Alternatively, consider an I.T services company that has a partnership with a
globally recognized and credible brand e.g., IBM, Salesforce, etc.
So long as those partnerships are a constrained resource and a
differentiator in a customer’s willingness to pay, then, this acts as a
barrier to entry.
New entrants lacking that credibility from that partnership may need to accept
higher customer acquisition costs or lower revenue,
making the value proposition of entry less desirable.
Network effects are another constrained resource and barrier to entry.
Social and dating platforms benefit from these. The more users on a platform,
the more benefits there are to the participants.
For example, once LinkedIn has millions of users a new entrant will have a high barrier to
entry and require a new and particularly unique and compelling value proposition
to have people join its platform.

Protecting against new entrants
Protecting against new entrants is enhanced by increasing barriers to entry to the extent that you in your business or as a member of an industry association can legally and morally do. Some actions that fit into the category are:
-
Reputation and brand
It takes time to build a reputation, so building trust within your business ecosystem with partners, suppliers and customers can act as a barrier to entry.
-
Increase customer affinity
Give your customers less reason to switch and more reason to stay with your business / value proposition.
Loyalty programs are an obvious tactic used to increase customer affinity in multiple industries. As customers get rewards for loyalty they are less likely they are to churn
In a chapter coming up, we look at building customer delight. The more delight you can deliver to customers, then the more difficult it is for a new entrant to entice your customers away.
Lock in - many platforms once they have the customers data or processes in their possession the cost to move to another platform is time-consuming and costly for the customer. Hence, customers are less likely to churn. Examples: Facebook, Cloud platforms - AWS, Azure, Salesforce, ServiceNow
-
Limiting access to resources, skills, and relationships
Disable new entrant access to any intellectual property or know-how that may make it easier for them to take away your customers or target market. Amazon, for example patented the one-click purchase. Hence, no other e-commerce site can provide one-click purchase.
Patents and intellectual property protection can of course limit access to new entrants from using their resources to replicate your value proposition.
Other options
Establishing exclusive or limiting relationships with suppliers, partners, or other ecosystem players important to new entrants to help limit their capability to enter.
Limiting the skills available to new entrants. Professional bodies like the College of Surgeons do this by controlling the number of trained practitioners so as limit the supply and ensure surgeons incomes remain desirable. A semi-conductor company may acquire another, less so for the business, but to consolidate and have some influence over preventing new entrants from accessing the skills required.
Network effects
Network effects refers to any situation in which the value of a product, service, or platform depends on the number of buyers, sellers, or users who use it. Typically, the greater the number of buyers, sellers, or users, the greater the network effect—and the greater the value created by the offering.
Is there any option to add network effects to your value proposition?

Overcoming new entrant barriers
To overcome the barriers for new entrants, the strategy will need to find way to resolve or bypass new entrant barriers. This may occur in response to:
reduced regulations
improved technology breaking a resource barrier
a change in industry structure such as the collapse or significant faux par of a dominant player
- over-servicing of consumer needs in the segment which is coming at increased cost to consumers when a reduced capability offering at a lower price would satisfy some market segment(s).
Additionally, or alternatively, the new entrant can follow Clayton Christiansen’s Innovative disruption formula.
This has been more recently reiterated by Peter Theil most, particularly in his
"Competition is for losers" series.
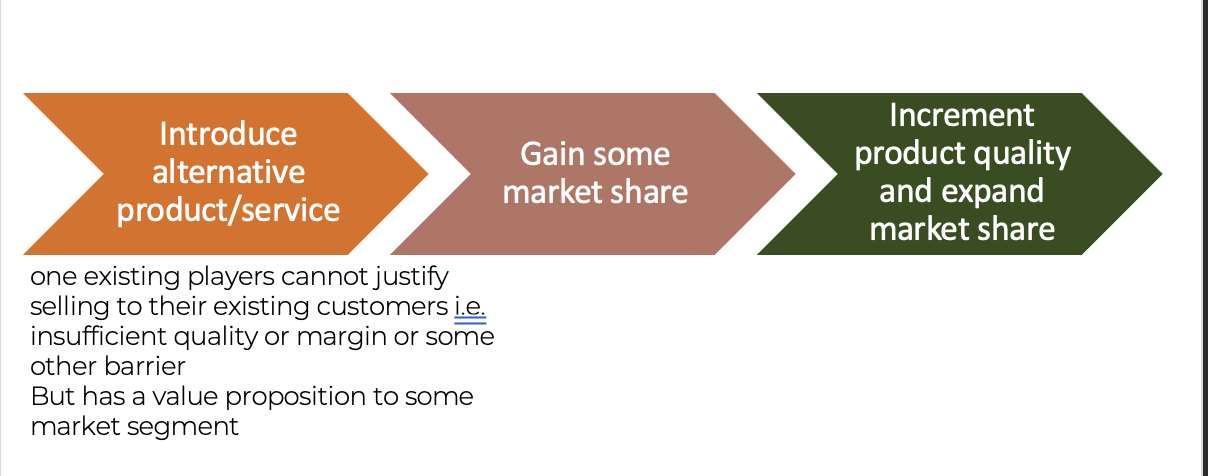
As the new entrant start at the low end of a market (low-end disruption) or creating a new market segment (new-market disruption) and claiming the least profitable or niche portion of little or no interest to the current players. Because the established, incumbent companies own the most profitable segments, they most likely won’t fight the entrant for unattractive market share. Once established in the low-end or new segment, then improve your offerings and move upmarket with increasing profitability. Continue to expand influence until once mainstream customers have widely adopted the entrant’s offerings in the mainstream market, then the disruption has occurred.
Continue with assessing buyer bargaining power
Assess and adjust the attractiveness of your where to play choice in StrategyCAD™
Try it Learn moreYou can try StrategyCAD™ free for 30 days to build your high performance strategy