In this section
-
Outline the elements of Assessment.
-
Apply the tools of Assessment in StrategyCAD™ to answer the question - Where are we today?
Assessment enables you and your strategic leadership team to assess where you are from multiple important points of view.

Assessment pre-conditions and purpose
The assessment section assumes that you and your leadership team have made / refreshed your external assessments for each of the Arenas in your where to play choice.
As shown in the screen shot above you can assess your current situation from
-
Internal
-
Ecosystem
-
Competitiveness
-
Customer
Points of view.
That is to win with your target customers you need the foundations of the right internal systems, structures, skills, style and so forth. You need an ecosystem to enable competitive delivery, and finally to understand where you stand relative to other options your target market has.
You can explore each assessment section in more details in the below sections.
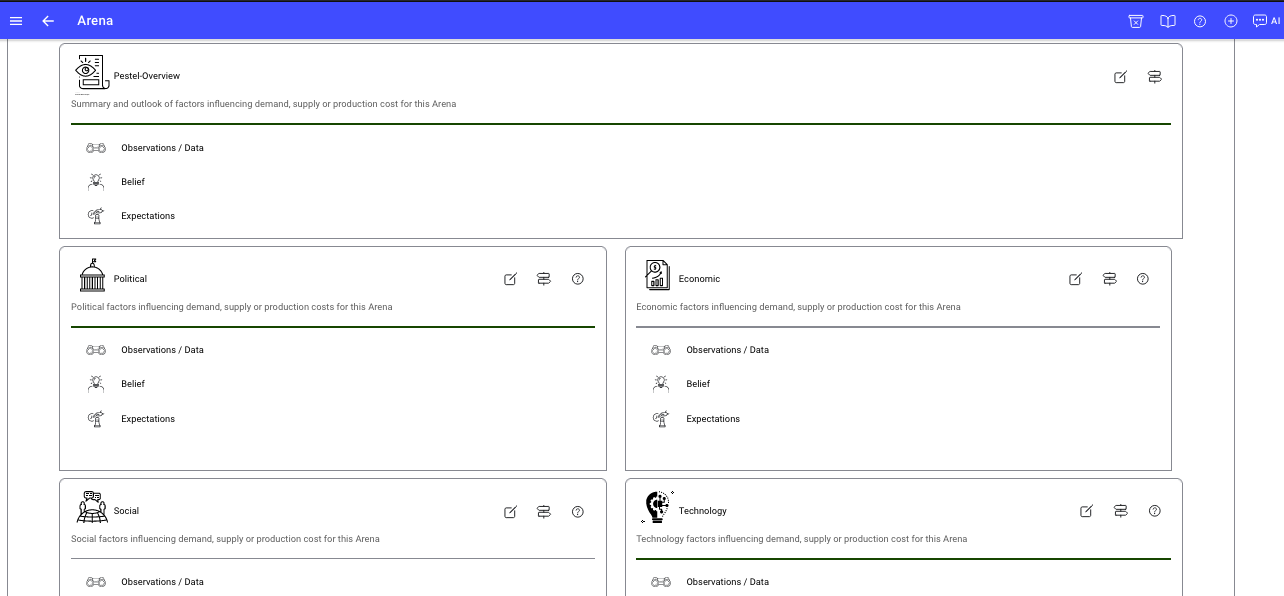
The overview is the overall summary which answers the question - Where are we today and where are we today relative to the Strategic choices? It summarises and draws conclusions from the insights from the other assessment areas.
To assist with communicating the overall assessment. The assessment summary component has the following default headings to provide a response in a format of We see, We believe, We expect
-
Observations - What we see
Which is summary of what the strategic leadership team are seeing either through observations, data, industry reports and so forth. -
Beliefs - What we believe
Based upon these observations, what does the strategic leadership team believe? -
Expectations - What we expect
Based upon these beliefs what does the leadership team expect is going to happen in the industry, customer needs, and the business?
You can quantitatively assess your internal environment using scorecards and scorecard comments.
StrategyCAD provides 3 different scorecards for your internal assessment.
-
Free form (as per your design) model
You can quantitatively assess your ecosystem using the scorecards for one or more of supply chain, partnerships or free form (an assessment of your design)
Ecosystem assessment - to determine capability in ecosystem relationships to deliver your unique value and delight customers
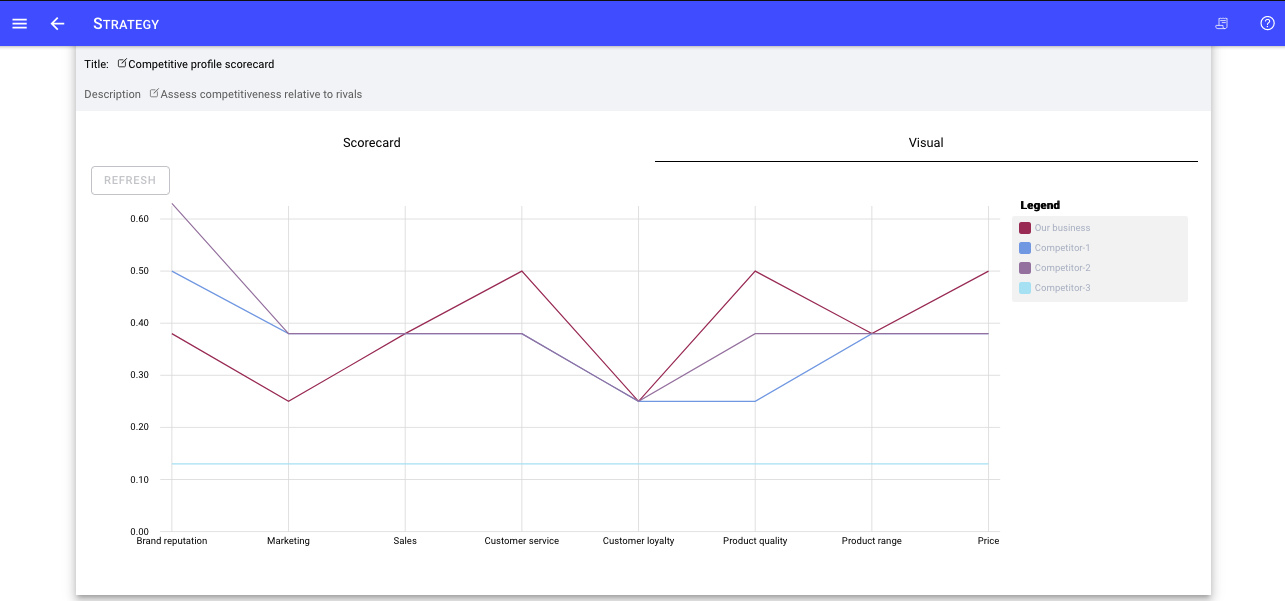
The Competitor assessment enables you and your strategy team to evaluate how your business is doing relative to competitors
-
Competitor profile - assess competitive capability in general terms including Marketing, Sales product range, customer service and so forth
-
Product profile - assess competitive capability of your products / services in terms of functional, social and emotional needs, reputation, quality attributes.
-
Competitive landscape - Market positions, growth, innovation capability etc.
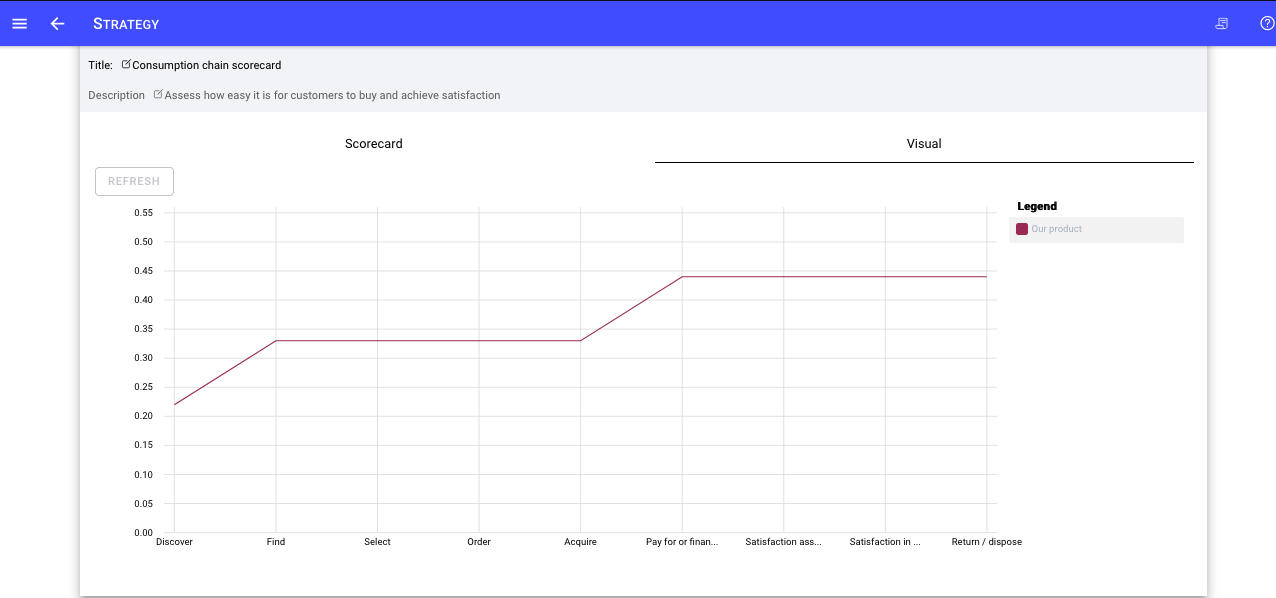
The Customer assessment enables you and your strategy team to evaluate how your business is doing relative to winning with and delighting customers
-
Customer assessment - evaluate customer awareness, engagement needs satisfaction, retention, trust and more
-
Consumption chain - A consumption chain refers to the series of steps that a customer goes through when purchasing and using a product or service. It includes all the touchpoints and interactions that a customer has with a business, from initial awareness and consideration to post-purchase evaluation and advocacy. A consumption chain assessment enables you to understand the customer journey and identify opportunities to optimize and improve the customer experience. By mapping out the various touchpoints and interactions, businesses can identify pain points and areas for improvement, develop targeted marketing and sales strategies, and tailor their products or services to better meet the needs of their customers. Ultimately, understanding the consumption chain is critical for creating a customer-centric business strategy that maximizes customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy.
-
Value delivery chain - Assess how well your value delivery system is doing in delivering your unique value proposition.
Scorecard models
McKinsey 7S Model
Purpose
McKinsey & Company, a management consulting firm, created the 7-S model to help client companies successfully implement their strategies. It was later featured in the book In Search of Excellence, by former McKinsey consultants Thomas J. Peters and Robert H. Waterman. The model highlights 7 important elements of organizational design to create the alignment necessary to implement the business strategy. The 7 S’s are: Strategy, Structure, Systems, Skills, Staffing, Style and Shared Values.
Why alignment?
Individuals and businesses frequently define worthy aspirations and goals, but are subsequently unsuccessful in sustaining the momentum to achieve them. This absence of momentum is a consequence of insufficient alignment from one or multiple sources. The absence of alignment in business strategy execution results in people and processes being insufficiently positioned to implement the strategy. The 7S model is an enduring framework to enable you to comprehensively assess your current internal alignment to implement your strategy and redefine or update your organizational design to achieve your evolved strategy.
Each S described
An overview of each S is outlined below
Strategy
Strategy summarises the strategic choices and importantly defines who the business will serve and how it will win by satisfying or delighting its' customers better than any alternative.
Structure
Structure deals with defining how the organizational is structured to be able to deliver and sustain its' value proposition?. Structure in addition to reporting lines tells you about how the structure supports people and teams to win and delight customers.
Structural questions include will the business be structured based upon geography, or by function e.g. sales, marketing, research and development, or by value streams, by product or product category or some combination of those? What organizational structure enables the business to deliver on its strategic choices and operate its value delivery chain?
Systems
Systems is broader than technology systems, but considers the processes in place (current assessment) or necessary to be in place to enable the business to fulfill its strategic choices, mitigate threats, and fulfill opportunities.
Shared values
Values that guide conduct and decision making to reinforce what the business is aiming to achieve in both its' customer and business aspirations
Skills
Skills capture the current (if a current 7S assessment) or necessary (future or target organizational design) abilities of individual employees as well as the capabilities of the firm. Skills capture the things a firm does well and the tools and technologies it uses to do them.
Style
Style speaks to "How we do things around here" and the example and approach that the business leaders and management take in leading the business, as well as how this influences performance, productivity, and corporate culture.
Staff
How people in the business are recruited, onboarded, engaged, developed and retained.
Find out more
Visit the McKinsey 7S website
Galbraith Star model
Purpose
The Star model helps you and your team successfully implement your strategies. . The model highlights 5 important elements of organizational design to create the alignment necessary to implement the business strategy. The 5 elements are: Strategy, Structure, Processes, Rewards and People.

Why alignment?
Individuals and businesses frequently define worthy aspirations and goals, but are subsequently unsuccessful in sustaining the momentum to achieve them. This absence of momentum is a consequence of insufficient alignment from one or multiple sources. The absence of alignment in business strategy execution results in people and processes being insufficiently positioned to implement the strategy. The Star model is an enduring framework to enable you to comprehensively assess your current internal alignment to implement your strategy and redefine or update your organizational design to achieve your evolved strategy.
Each elements is briefly described
An overview of each S is outlined below
Strategy
Strategy summarises the strategic choices and importantly defines who the business will serve and how it will win by satisfying or delighting its' customers better than any alternative.
Structure
Structure deals with defining how the organizational is structured to be able to deliver and sustain its' value proposition?. Structure in addition to reporting lines tells you about how the structure supports people and teams to win and delight customers.
Structural questions include will the business be structured based upon geography, or by function e.g. sales, marketing, research and development, or by value streams, by product or product category or some combination of those? What organizational structure enables the business to deliver on its strategic choices and operate its value delivery chain?
Processes
Considers the essential processes in place (current assessment) or necessary to be in place (future state) to enable the business to fulfill its strategic choices, mitigate threats, and fulfill opportunities.
Rewards
Rewards to guide conduct and decision making to reinforce what the business is aiming to achieve in both its' customer and business aspirations
People
How people in the business are recruited, onboarded, engaged, developed and retained. Additionally, considers the skills avaiable (if a current assessment) or necessary (future or target organizational design) abilities of individual employees as well as the capabilities of the firm. People assessment enables the identification of people assets to understand what the busienss does or could do well.